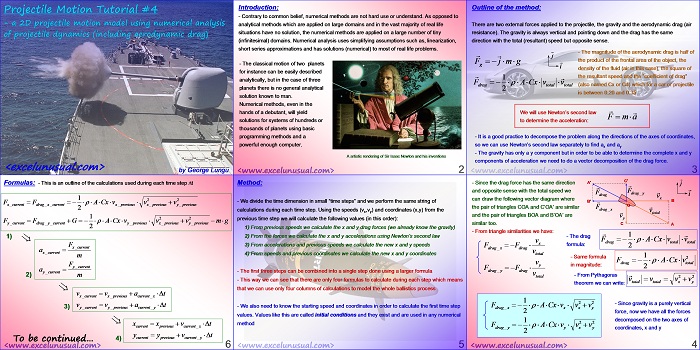
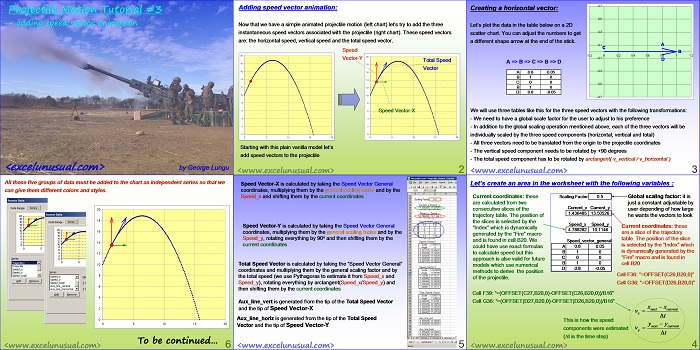
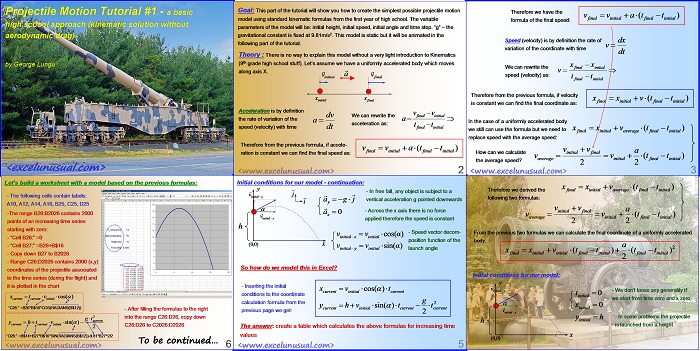
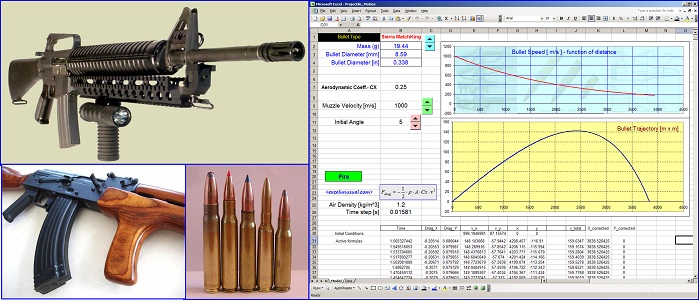
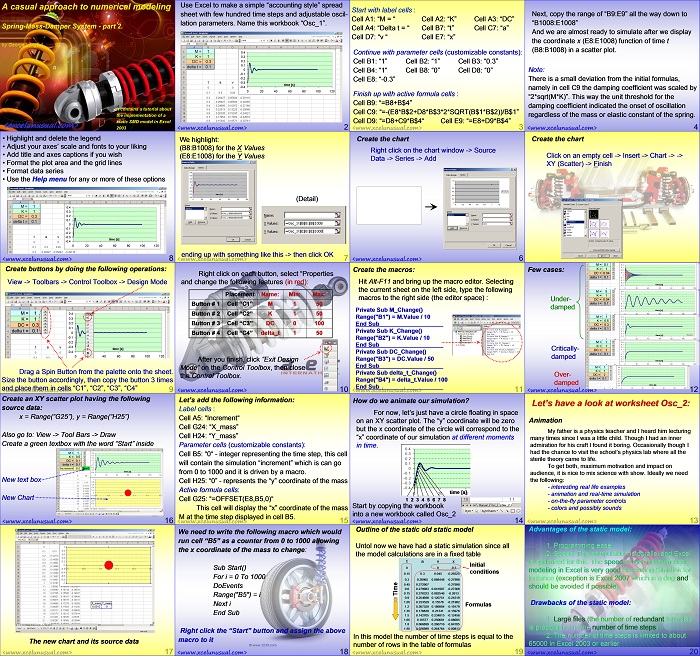
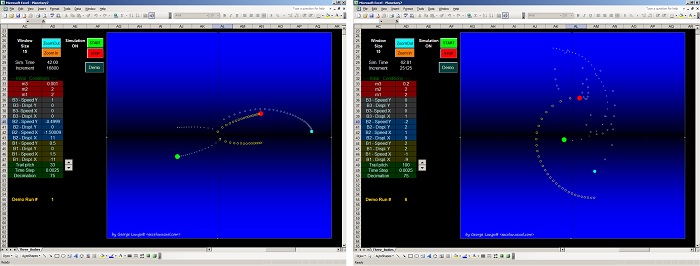
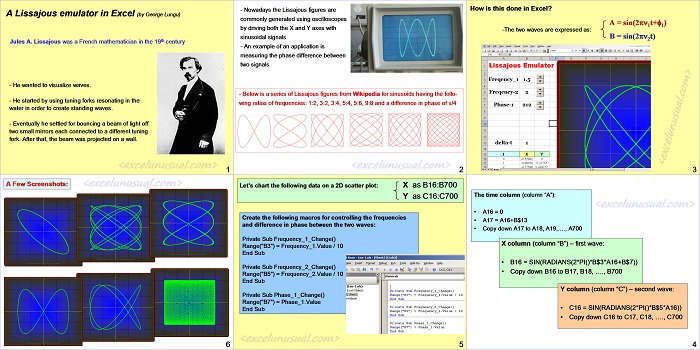
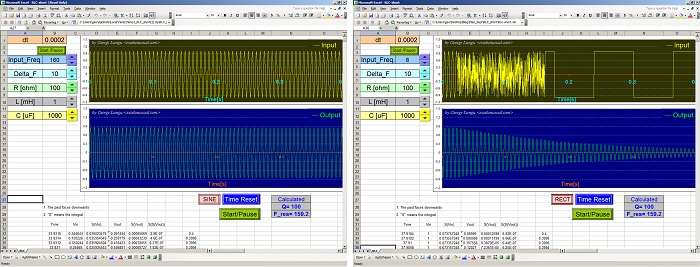
This tutorial simplifies the previous model and manages to describe the (x,y) flight coordinates using just two formulas placed on columns D and E. A custom VBA trajectory function will be introduced in the next section which preserves the effects of gravity and aerodynamic drag. [sociallocker][/sociallocker] Projectile Motion Tutorial #5 by George Lungu – a 2D projectile motion model of projectile dynamics including… Read More... "2D Projectile Motion Tutorial #6"