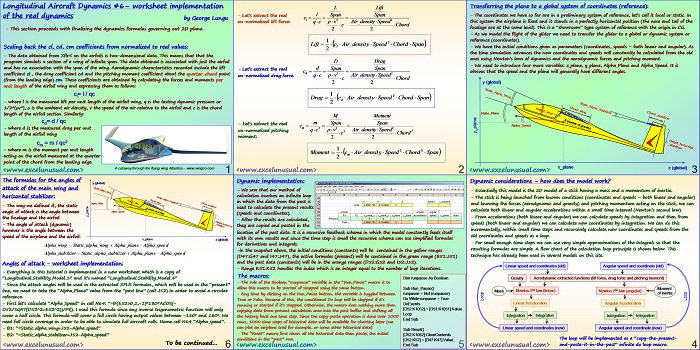
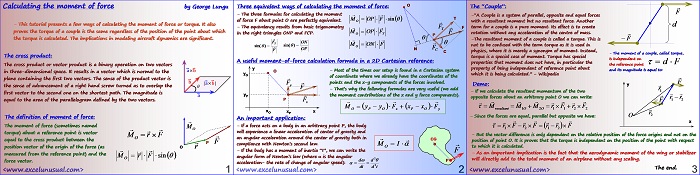
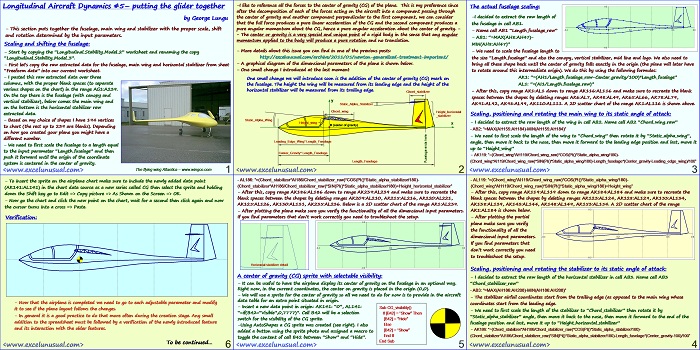
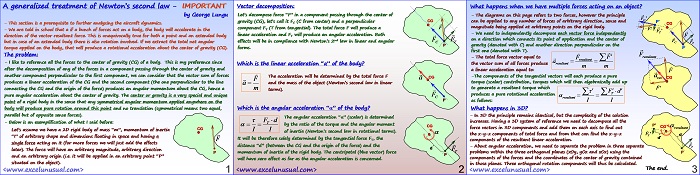
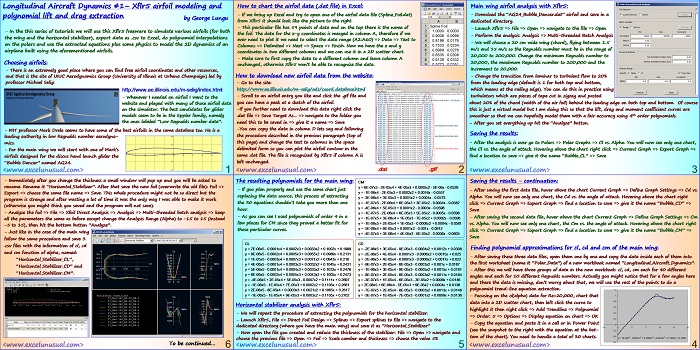
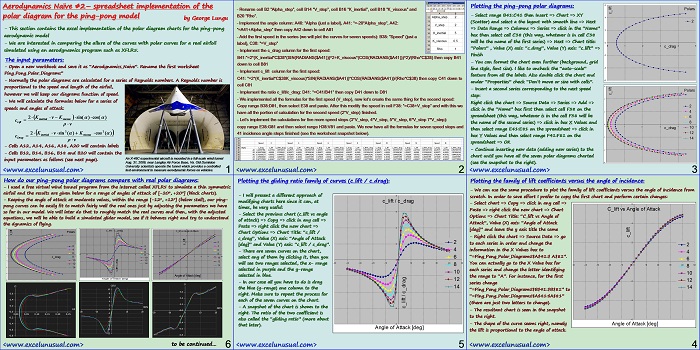
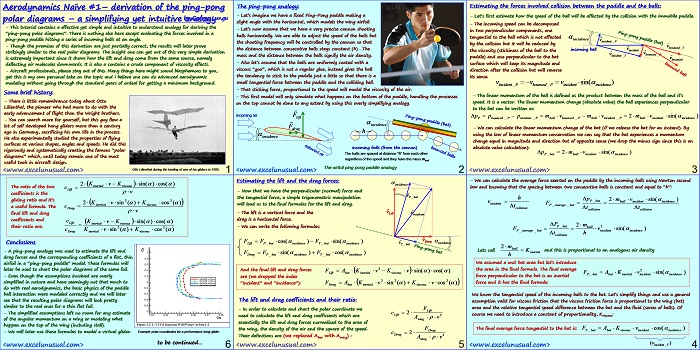
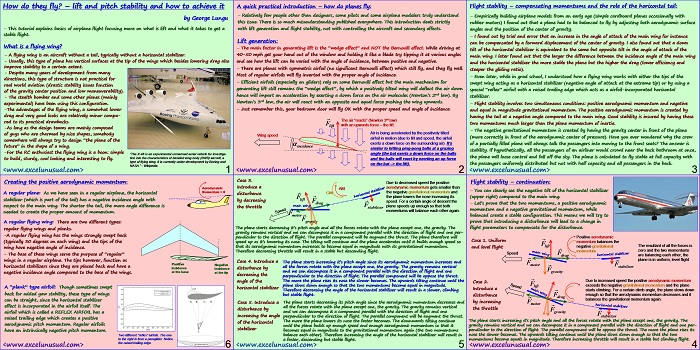
This section continues the worksheet implementation of the dynamics formulas. [sociallocker][/sociallocker] Longitudinal Aircraft Dynamics #7- worksheet implementation of the real dynamics by George Lungu – This section continues with the dynamics formulas governing our 2D plane and their worksheet implementation. Some Reynolds number corrections: – We introduced one single named cell for the Reynolds number (Re) when in fact there… Read More... "Longitudinal Aircraft Dynamics #7 – worksheet implementation of the dynamics equations (b)"